With ‘Archetypes’, Cannabis Industry Meets Customers in the Open Market

The Week That Was: Removal of Pete, Jeff Sessions Seen as Boons for Cannabis
November 10, 2018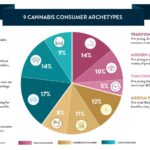
9 Cannabis Consumer Archetypes
November 19, 2018By J.J. McCoy, Senior Managing Editor, New Frontier Data
A foundational tent of setting up any business is understanding you one’s customer is, where they are, and why they buy… Yet, given that until cannabis laws began transitioning from prohibition to medical then to full adult use many cannabis consumers worked hard to maintain their invisibility and anonymity, much of popular culture image of cannabis consumers was drawn from stereotypes and caricatured a particular type of consumer, and not reflective of the diverse humanity that regularly consumes cannabis..
For too long, cannabis business owners have been forced to rely on anecdotal or subjective perceived consumer behavior. But with the industry generating nearly $10 billion in sales throughout 2018, the surging growth of the industry and the rapidly evolving preferences and behaviors of cannabis consumer have dramatically heightened the need understand who is buying all this cannabis and understand what motivates their purchases.
As Mark Twain once said, “All generalizations are false, including this one.” Displacing the generalizations about cannabis consumers with meaningful, insightful facts was the inspiration behind New Frontier Data’s latest industry study, The 2018-2019 Cannabis Consumer Report: Archetypes, Preferences & Trends, designed to identify, quantify, and individuate consumer behavior, motives, and buying patterns of key, objective demographic customer groups within the legal cannabis industry.
New Frontier Data teamed up with point-of-sale platform MJ Freeway to publish a comprehensive study based on nearly $5 billion worth of transactions recorded since 2015 and an online survey of more than 3,100 cannabis consumers across the U.S… By identifying and analyzing the respective perspectives of nine distinct consumer archetypes demonstrating behaviors and consumption patterns, the report is a substantive appreciation of how and why consumers buy, consume, and experience cannabis. For example:
- The top three reasons why consumers use cannabis are for relaxation (66%), stress relief (59%) and to reduce anxiety (53%). Nevertheless, small percentages use cannabis for a long list of reasons. including to improve their sleep, treat medical conditions, enjoy social experiences, and stimulate creativity.
- Four in 10 consumers – both medical and recreational – report using cannabis for pain management, reflecting the growing research on the efficacy of cannabis for pain management, and its potential to address the national epidemic regarding opioids.
- While joints and pipes remain the preferred way to consume cannabis for half the market (53%), demand for non-flower products (including concentrates, vaporizers, and edibles) has grown dramatically among consumers in both legal and non-legal markets.
As detailed in today’s CannaBit, the consumer archetypes include three high-frequency consumption groups, three moderate-frequency consumption groups, and three low-frequency consumption groups. In addition to frequency of use, the consumer categories differ by their primary cannabis sources, spending habits, preferred products, openness about use, reasons for use, and many other variables.
As another wise person once said, “A satisfied customer is the best business strategy of all.” At last, there’s a studious opportunity for the legal cannabis industry to understand their customers, and to better satisfy them.